Ublox SAM-M8Q GPS Board
Overview
The Boardoza Ublox SAM-M8Q is a precision-engineered GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) solution designed around the industry-leading u-blox SAM-M8Q concurrent positioning engine. This module distinguishes itself with its embedded wide-band patch antenna, which utilizes a specialized "Smart Antenna" architecture to deliver omnidirectional reception and superior gain, even in RF-hostile environments.
Capable of acquiring signals from up to three satellite constellations simultaneously (GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo), the board offers exceptional positioning accuracy and reliability compared to single-constellation receivers. With its dual-interface design (UART and I2C) and wide input voltage compatibility, it serves as a versatile geospatial anchor for avionics, autonomous robotics, and precision asset tracking systems.

Core Technical Specifications
The module is defined by the following operational parameters:
GNSS Engine: 72-channel u-blox M8 architecture supporting concurrent reception of GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo.
Antenna Topology: Integrated wide-band patch antenna with an omnidirectional radiation pattern, eliminating the need for external RF circuitry.
Update Rate: Supports up to 18 Hz in single-GNSS mode and 10 Hz when using concurrent GNSS, enabling high-dynamic tracking.
Sensitivity: Achieves a tracking sensitivity of -165 dBm and a cold-start acquisition sensitivity of -146 dBm.
Supply Voltage: engineered for flexibility with a simplified input range of 3.3V to 5.5V DC.
Communication Interfaces: Features both UART (TTL) and I2C buses for broad microcontroller compatibility.
Time Pulse Accuracy: Provides a highly precise PPS (Pulse Per Second) signal with ±30ns RMS accuracy for system time synchronization.
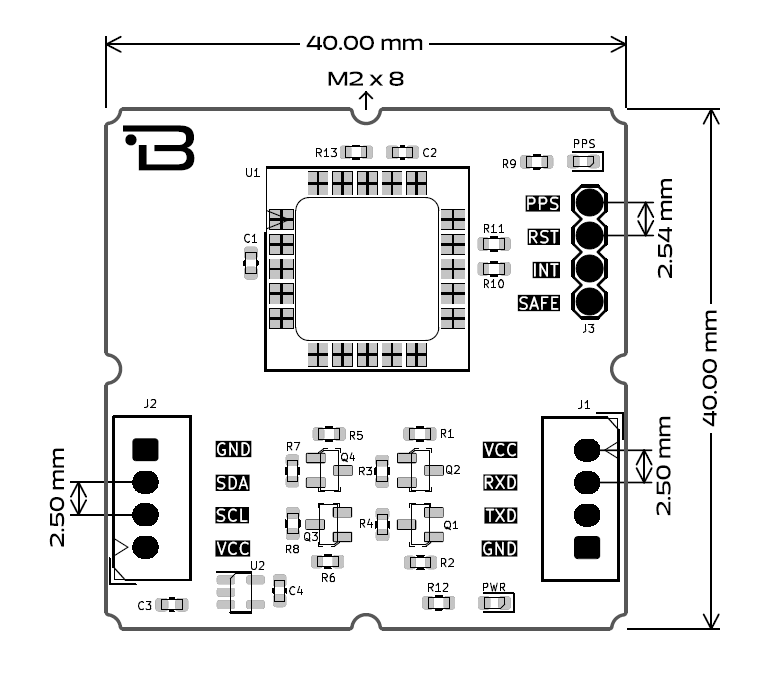
Physical Dimensions: A standardized 40 mm x 40 mm footprint with mounting holes for secure chassis integration.
Key Engineering Features
Concurrent Multi-GNSS Reception
Unlike legacy GPS-only modules, the SAM-M8Q leverages concurrent processing to track multiple constellations simultaneously. This "Multi-GNSS" capability significantly increases the number of visible satellites, improving position lock stability in "urban canyons" or obstructed horizons where a single constellation might fail.
RF Interference Mitigation
The module integrates a high-performance SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) filter and a low-noise amplifier (LNA) directly in the RF front-end. This architecture provides exceptional immunity against jamming and RF noise from collocated peripherals like cellular modems or motor drivers, ensuring data integrity in complex electromechanical systems.
Embedded Smart Antenna
The onboard patch antenna is tuned for optimal performance independent of the ground plane size. This "design-in" readiness reduces the complexity of RF impedance matching during the integration phase, allowing engineers to treat the GPS subsystem as a "black box" component.
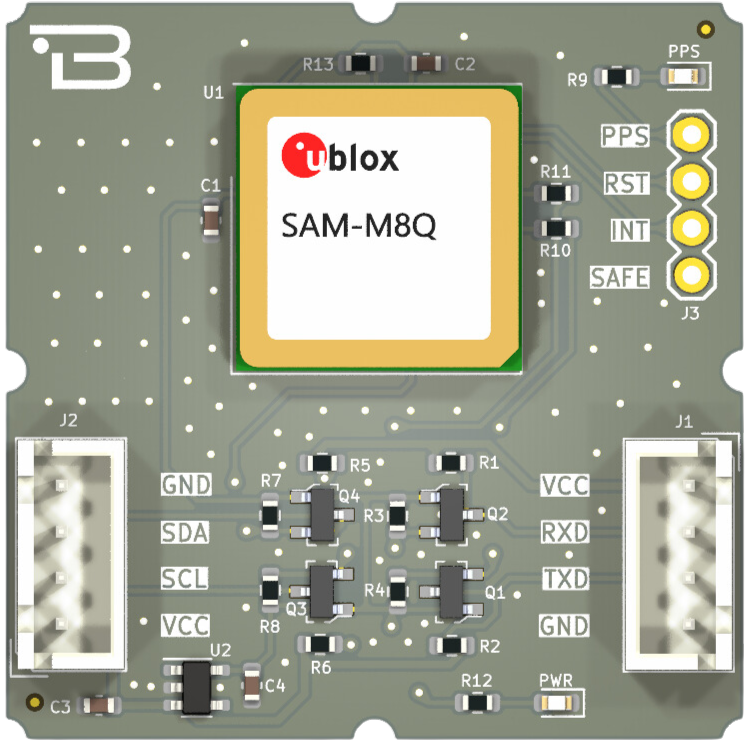
Hardware Interface and Signal Mapping
The board provides access to power and data lines via standard 2.54mm pitch headers, organized into logical groups:
Communication Interfaces
VCC: Main power supply input (3.3V - 5.5V).
GND: Common system ground.
TXD: UART Transmit line (Outputs NMEA stream to MCU).
RXD: UART Receive line (Inputs configuration commands from MCU).
SDA: I2C Serial Data line for bus-based communication.
SCL: I2C Serial Clock line.
System Control Pins
PPS: Pulse Per Second output. Delivers a high-precision logic pulse synchronized to atomic GPS time, essential for data logging timestamps.
RST: Active-low hardware reset pin. Used to externally reboot the GNSS engine.
INT: External Interrupt input. Can be used to wake the module from power-save modes or for time-aiding injection.
SAFE: Reserved pin for SAFEBOOT_N functionality, used during firmware updates or recovery procedures.
Applications
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Provides stable positioning and "Return-to-Home" coordinates for drones.
Precision Agriculture: Enables geofenced autonomous steering for robotic farming equipment.
Fleet Telematics: Tracks vehicle location, speed, and heading for logistics management.
High-Altitude Ballooning: capable of operating at high altitudes (up to 50,000m depending on flight mode configuration).
Board Dimensions:
Ready to integrate? You can purchase the Ublox SAM-M8Q GPS Board directly from our Online Store. Worldwide shipping is available for engineering samples and production batches.
Last updated
