TPS630702RNMT Breakout Board
Overview

Core Technical Specifications
Key Engineering Features
Seamless Buck-Boost Transition
Configurable Power Modes
Integrated System Protection
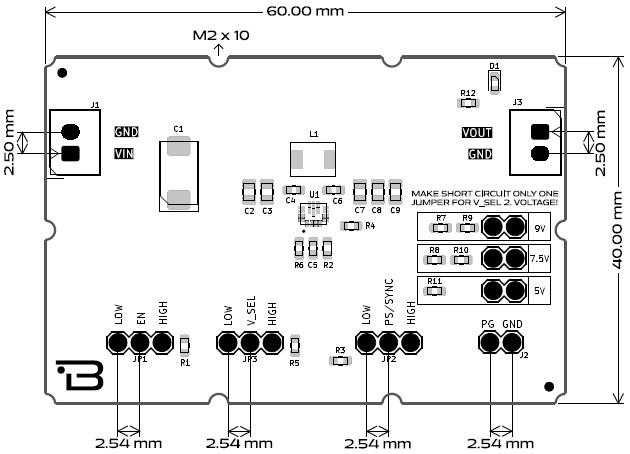
Board Pinout
J1 - Power Input Connector
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
J2 - Power Good (PG) Indicator
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
J3 - Output Connector
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
JP1 - Enable Control
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
JP2 - Power Save / Synchronization Mode
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
JP3 - Voltage Selection
Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
Voltage Selection Pads
Pad
Description
Applications
Board Dimensions
Last updated